Quick-start guide for MySQL DB database design
- New project
- Tables and columns
- Relationships and foreign keys
- Code generation
- Report creation
- Reverse engineering & visualization of existing databases
1. New project for MySQL
To create a new project, click the New icon on the main toolbar and select the MySQL project type.
2. Adding tables and columns to the project and diagram
New database tables can be added into projects by clicking Table on the toolbar and then by clicking the main diagram area. Another option you can use is to add an object via the context menu.
A new graphical object will appear on the diagram. Click the object to see details in the Right side panel. Editing in the panel is a fast way to easily change the structure and e.g. add columns to the table, create indexes, etc.
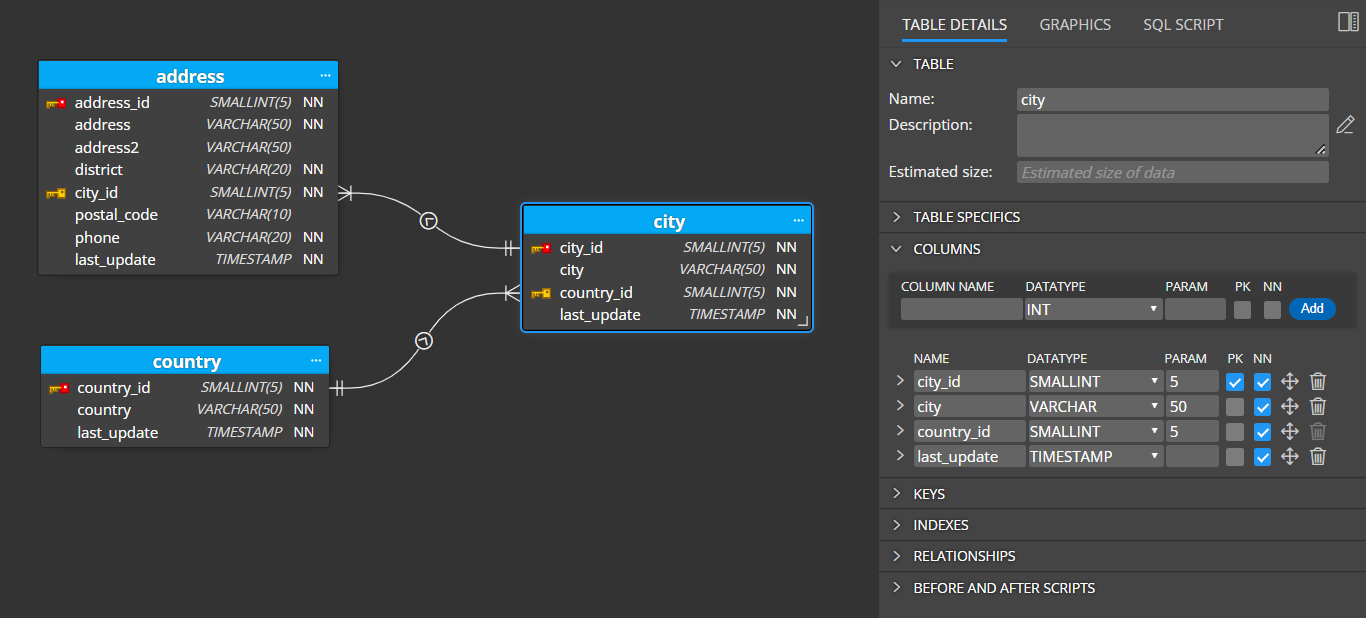
Alternatively, you can double click the graphics or right-click the item and choose Edit to open a larger modal form.
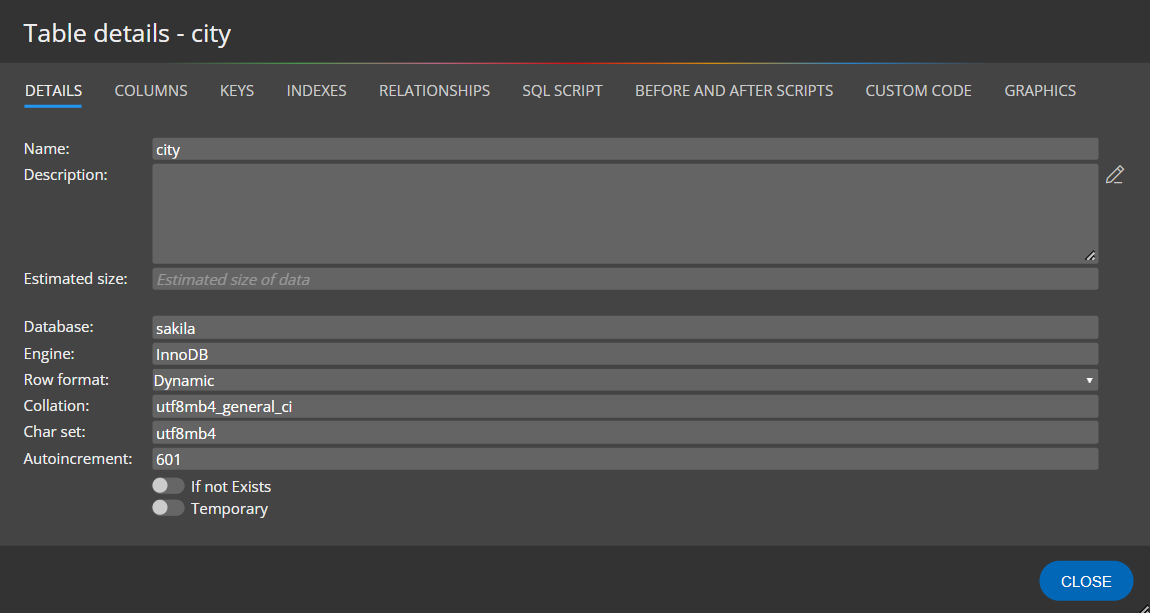
Table properties
Table settings can be specified in the section Details.
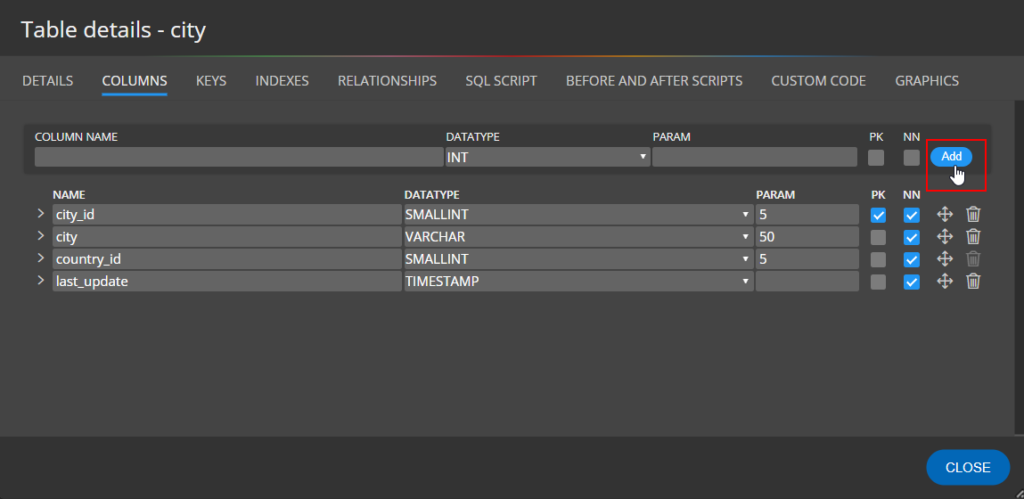
Columns
In section Columns, you can add new table columns. Specify new column name, datatype, and parameter and click Add.
- PK indicates the Primary key.
- NN represents the Not Null field.
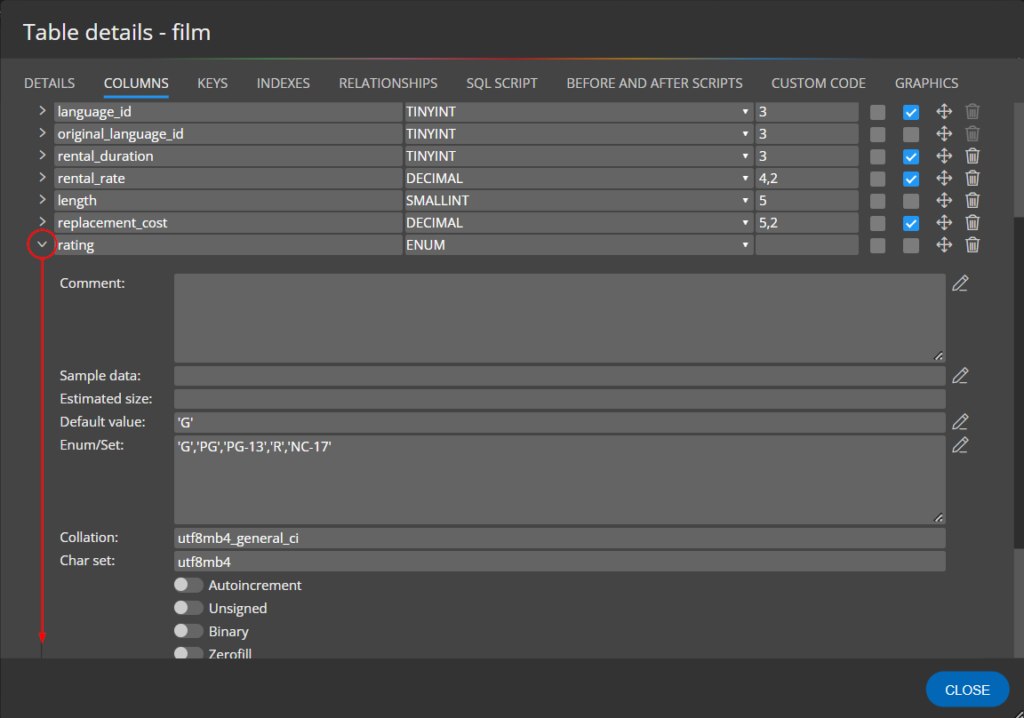
Column specifics
To access the area where MySQL column specifics can be set, click the arrow left to the column name.
3. Relationships and foreign keys
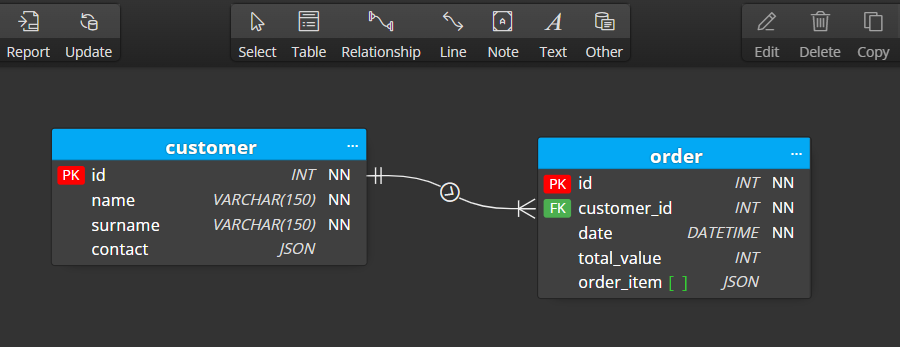
To create a new relationship between two database tables, click Relationship on the toolbar and then click parent and then child table.
When a new relationship is created, a foreign key appears in the child table automatically.
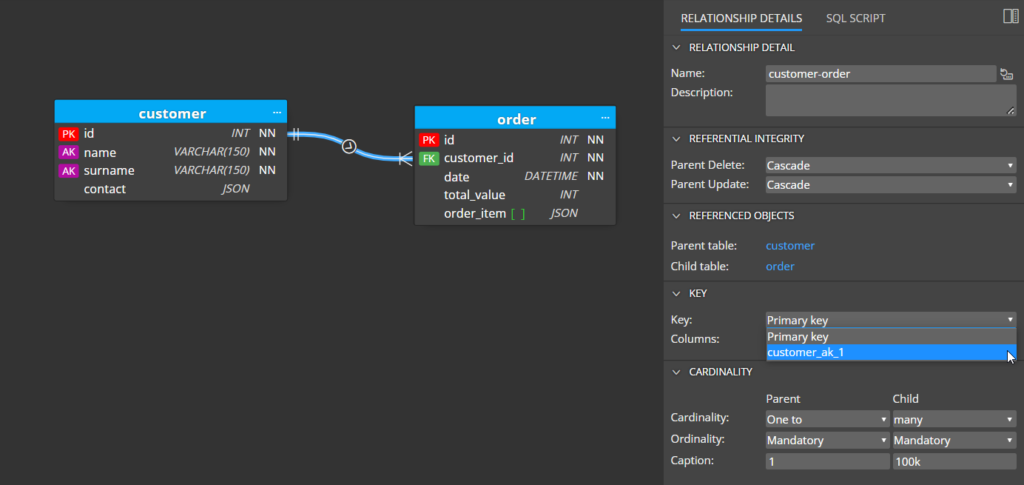
In the details section of relationships, you can specify referential integrity, used key (primary key or alternate key), and cardinality.
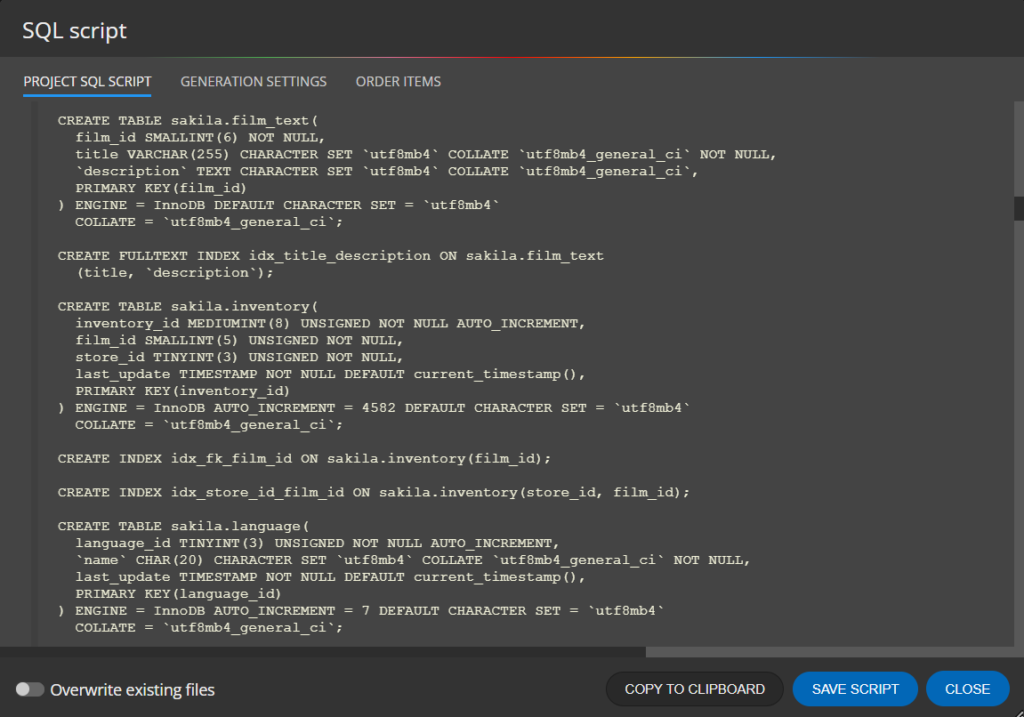
4. SQL Script & code generation
To preview the script for your MySQL database design, click the SQL Script tab on table detail.
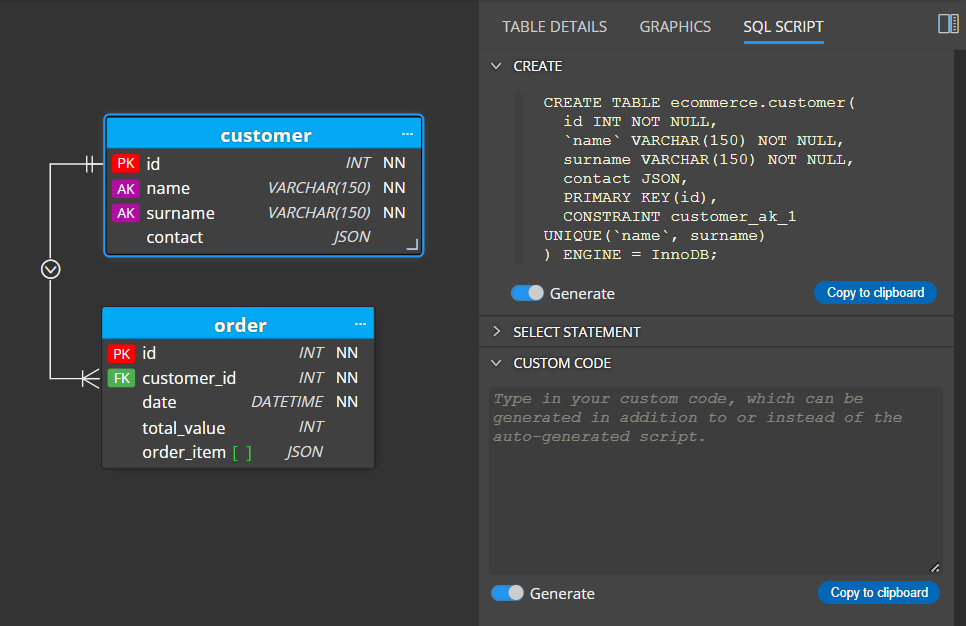
To save scripts to files, click the Script icon on the toolbar and then click Save script.
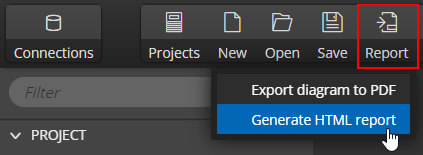
5. Report generation & export to PDF
One of the key features of our product is the ability to create simple documentation. Once you have your ER diagram ready, you can easily generate a PDF file or an interactive HTML report.
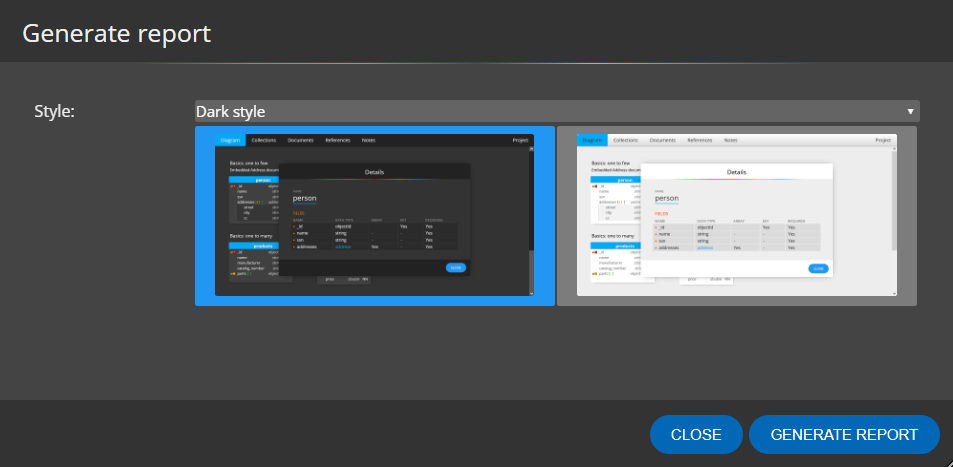
The report can be generated in dark or light style.
6. Reverse engineering and visualization of existing structures
If you already have a MySQL database and want to visualize it using an entity-relational diagram, you can create a new database connection and load the structure – all in a few steps. For more information, see Visualization of existing database structures.
#