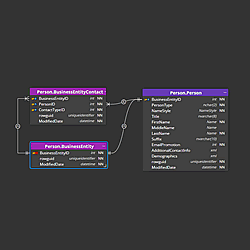
Looking for a fully visual way to work with a Postgres database?
In this guide, we’ll show you how to:
- Set up Postgres using Docker Desktop
- Create and manage your data model visually in Luna Modeler
- Generate SQL scripts from your data models
- Run them using pgAdmin
- Keep your database and data model in sync – all without touching the command line
Step-by-Step: How to Run Postgres in Docker
and Create Your Database Visually
In the following section, we’ll walk you through how to set up a PostgreSQL database using Docker Desktop. After that, you’ll learn how to work with your database using fully visual tools — no terminal needed at any point.
- Install Docker Desktop
To start, download and install Docker Desktop for your system (Windows, macOS, or Linux).
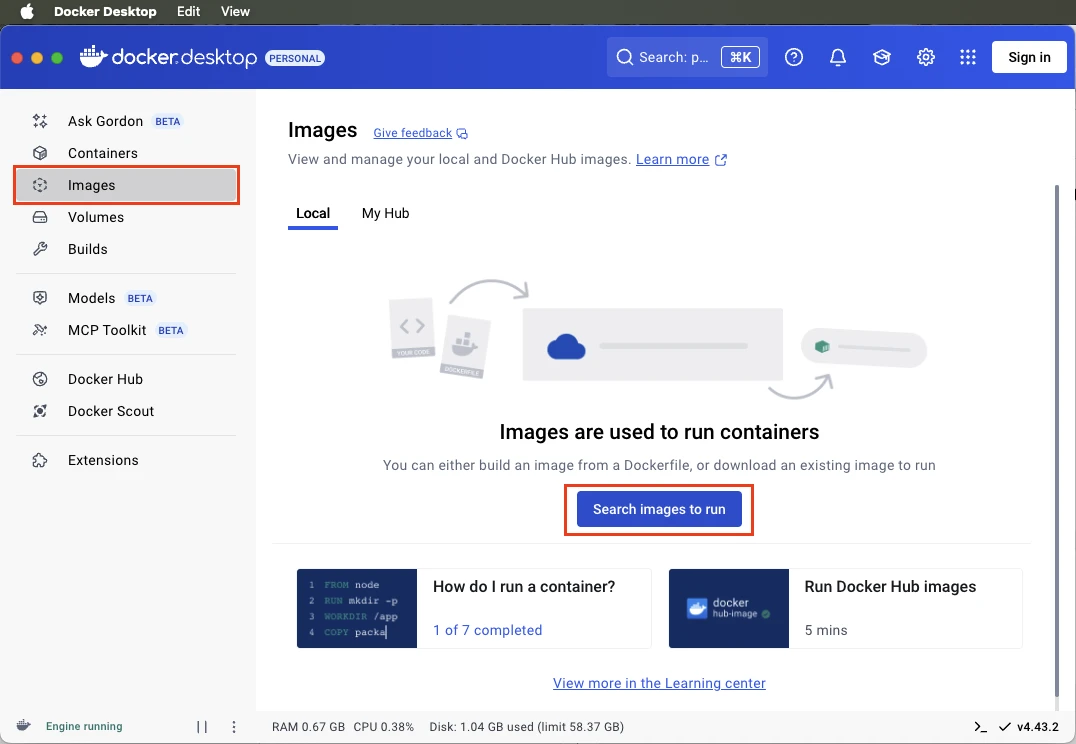
Once installed, open it. - Find the Postgres Image and Run a Container (Using Docker Desktop GUI)
Navigate to the Images tab and click the Search images to run button.
Search “postgres” and then click the Run button.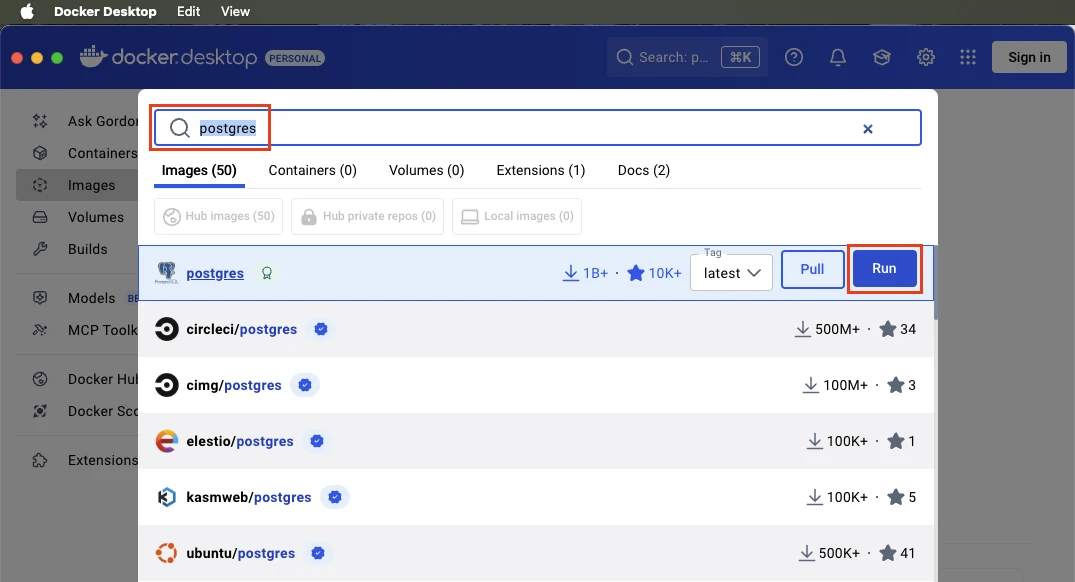
A new form opens. Define the Container name, Host port (the default for Postgres is 5432, but if the port is not available, set the value to some other value, e.g. 5433). Add a new environment variable POSTGRES_PASSWORD and type in the Value (this will be your password for the postgres user). Then click Run.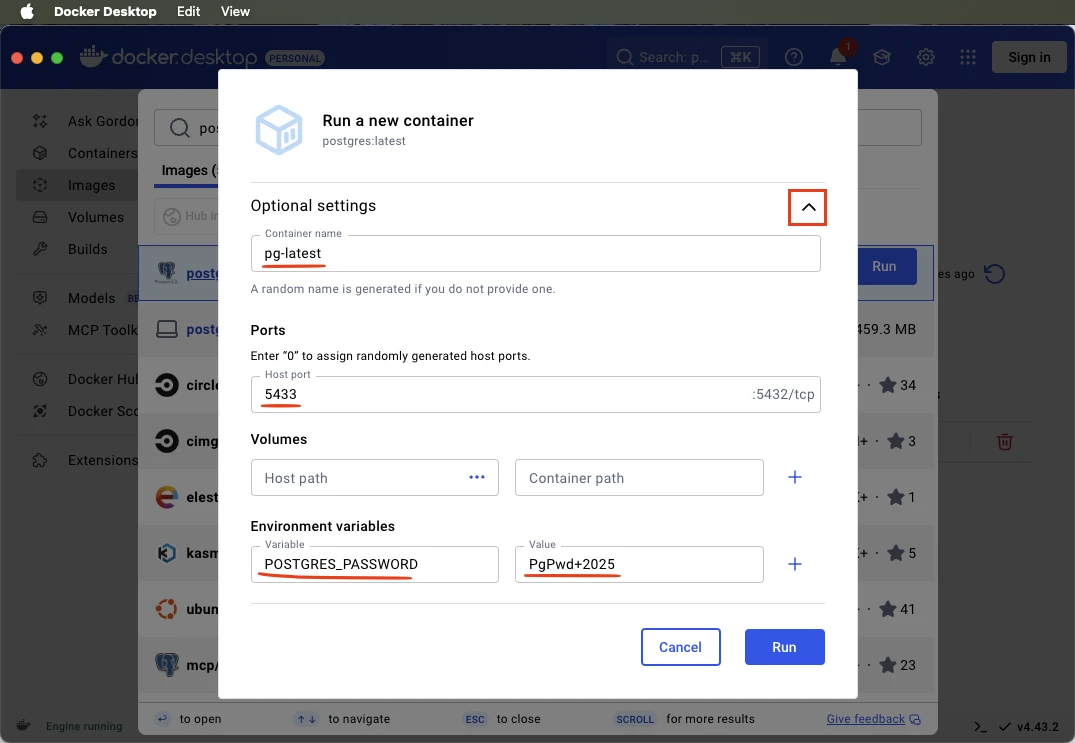
You should see the running container in the Containers section.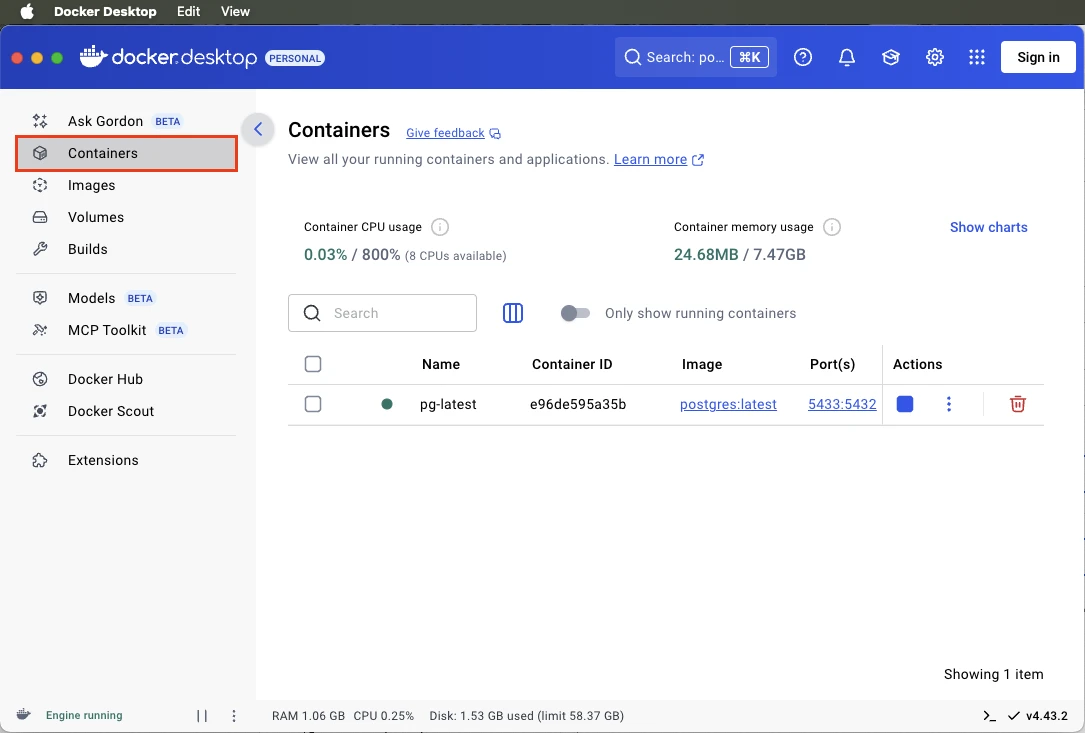
The database is now up and running. Let’s continue with creating a data model.
You might be wondering — why not just create the database structure directly? Why bother with a modeling tool? Well, the answer is simple. Think of it like building a house: you wouldn’t start laying bricks or installing windows without a complete architectural plan. The same logic applies to databases.
In fact, data modeling is an ongoing process. Many adjustments happen along the way, and – just like with a house – you typically wait until the blueprint is finalized before beginning construction. Likewise, it’s best to create your actual database only when the model feels complete.
Sure, you can build your database table by table. But planning it visually and thoroughly in advance is almost always more efficient – and definitely more convenient. - Create a Data Model in Luna Modeler
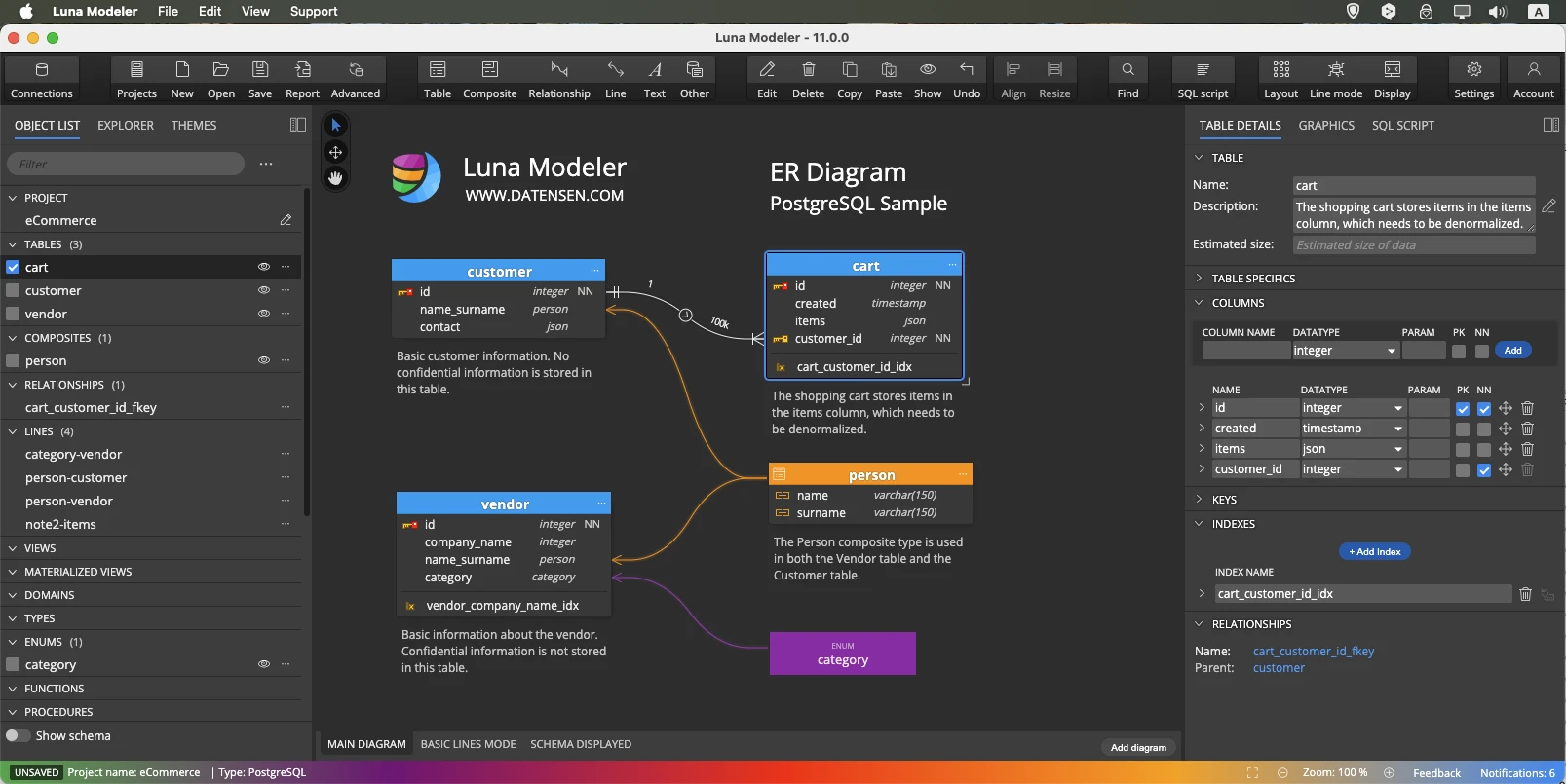
Download and install Luna Modeler. Create a new PostgreSQL project and start designing your database structure visually: add tables, define columns, relationships, enums, composites, add notes and subject areas and more. You can model everything without connecting to a database yet.
Download Luna Modeler - Generate SQL Script from Your Data Model
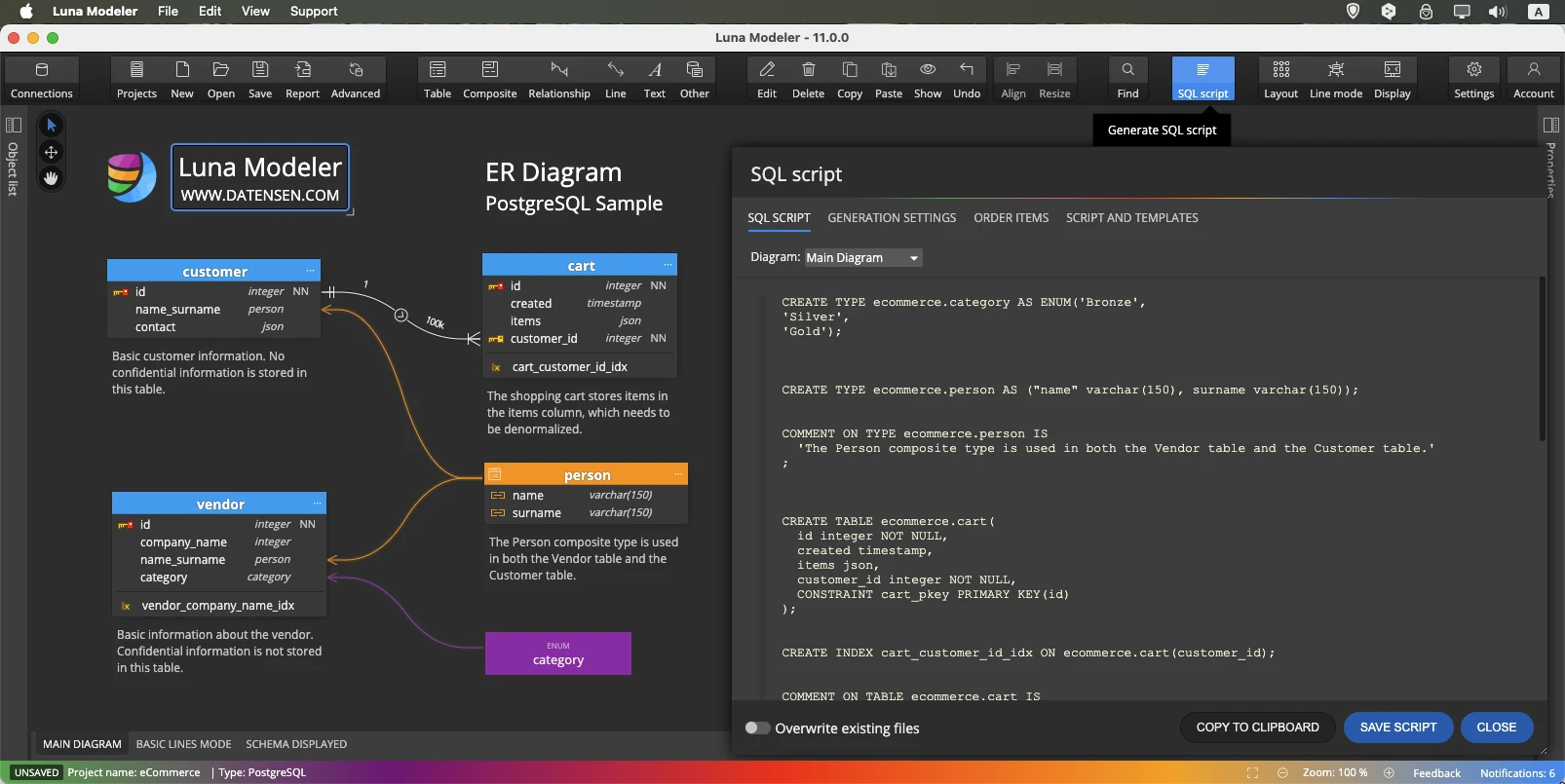
Once your data model is ready: Click the SQL Script button. Review the auto-generated script and save it to your computer.
- Run SQL Script in pgAdmin (Visual Tool)
Download pgAdmin and install it. Log in to pgAdmin using the credentials you set and
connect to your Postgres container.
Right click the Servers item and select Register – Server…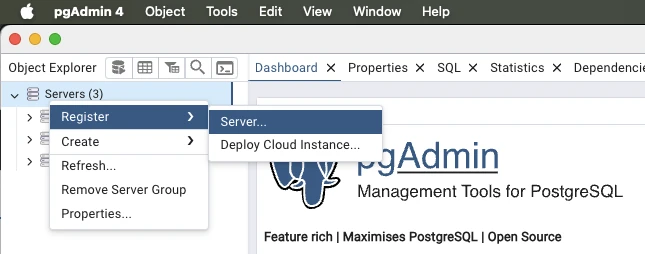
In section Connection, define the connection properties. If your installed both Docker Desktop and pgAdmin locally, specify the host as localhost. The port is in this case 5433 and the password is what we have specified in step 2 as the value of the POSTGRES_PASSWORD environment variable for the docker container.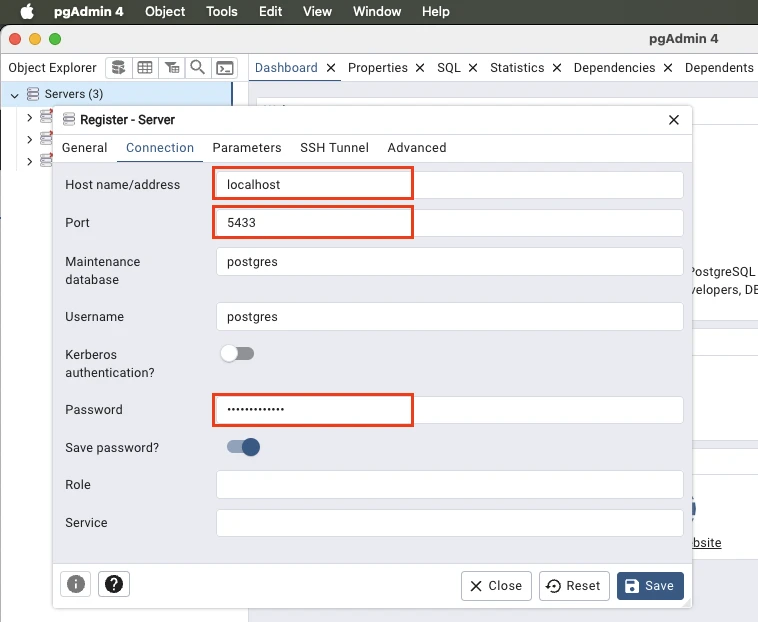
Now select existing database, or create a new database (ecommerce), use the public schema or create a new schema (ecommerce) and then open the Query Tool.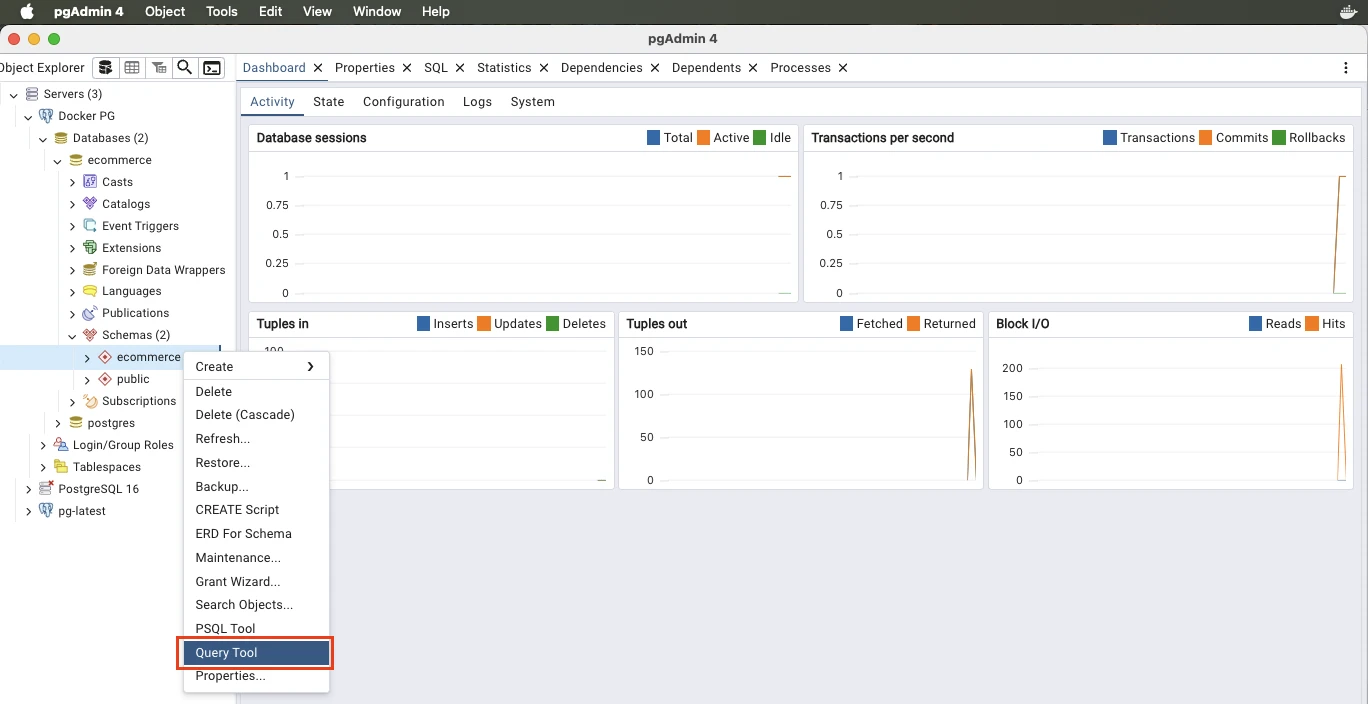
Paste the SQL script generated by Luna Modeler, and execute it.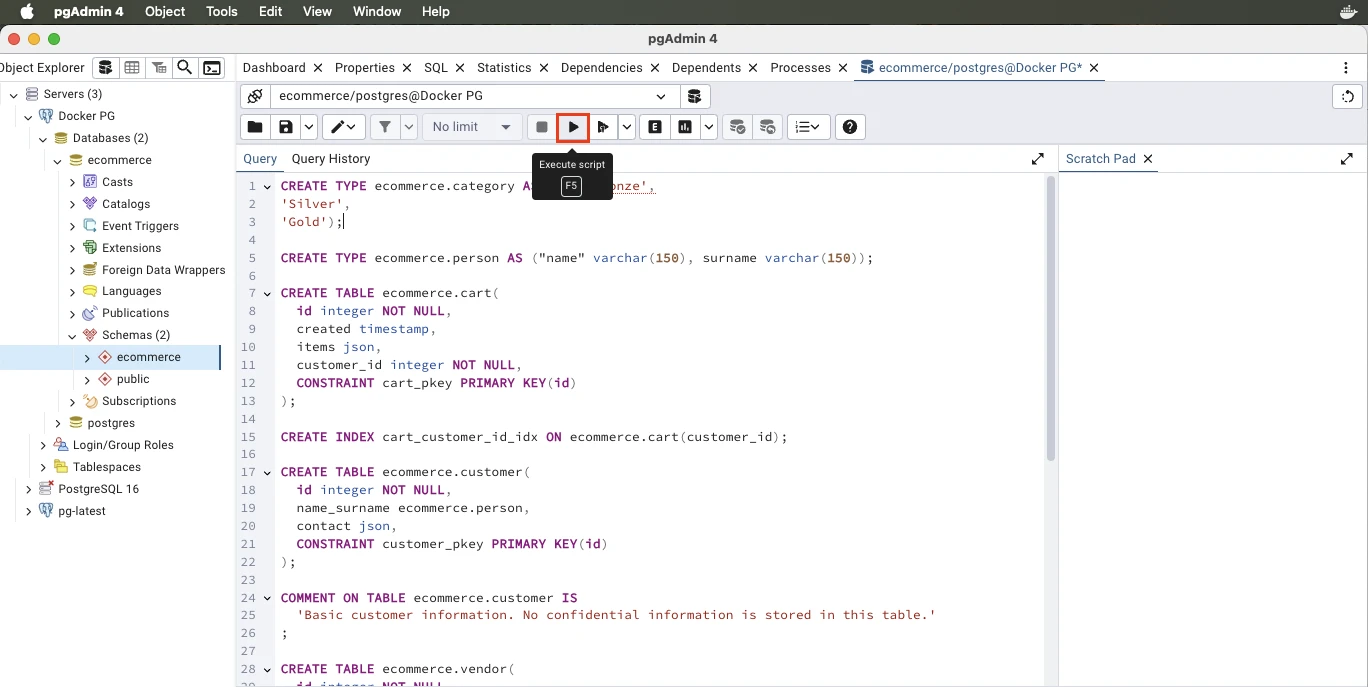
- Make Changes to Your Data Model
As your system evolves – especially in the early stages of development – changes are not just expected, they’re essential. That’s why it’s helpful to go back to Luna Modeler regularly to adjust your model: add new tables, modify columns, change data types, define relationships, or update constraints.
- Generate Sync Script
In Luna Modeler, click the Advanced button and choose Generate Synchronization SQL
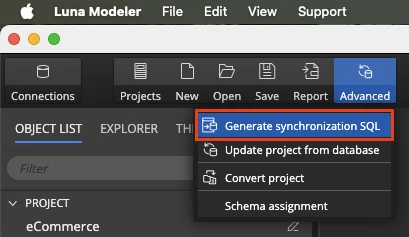
Compare the data model to the database and generate SQL Script for the detected differences.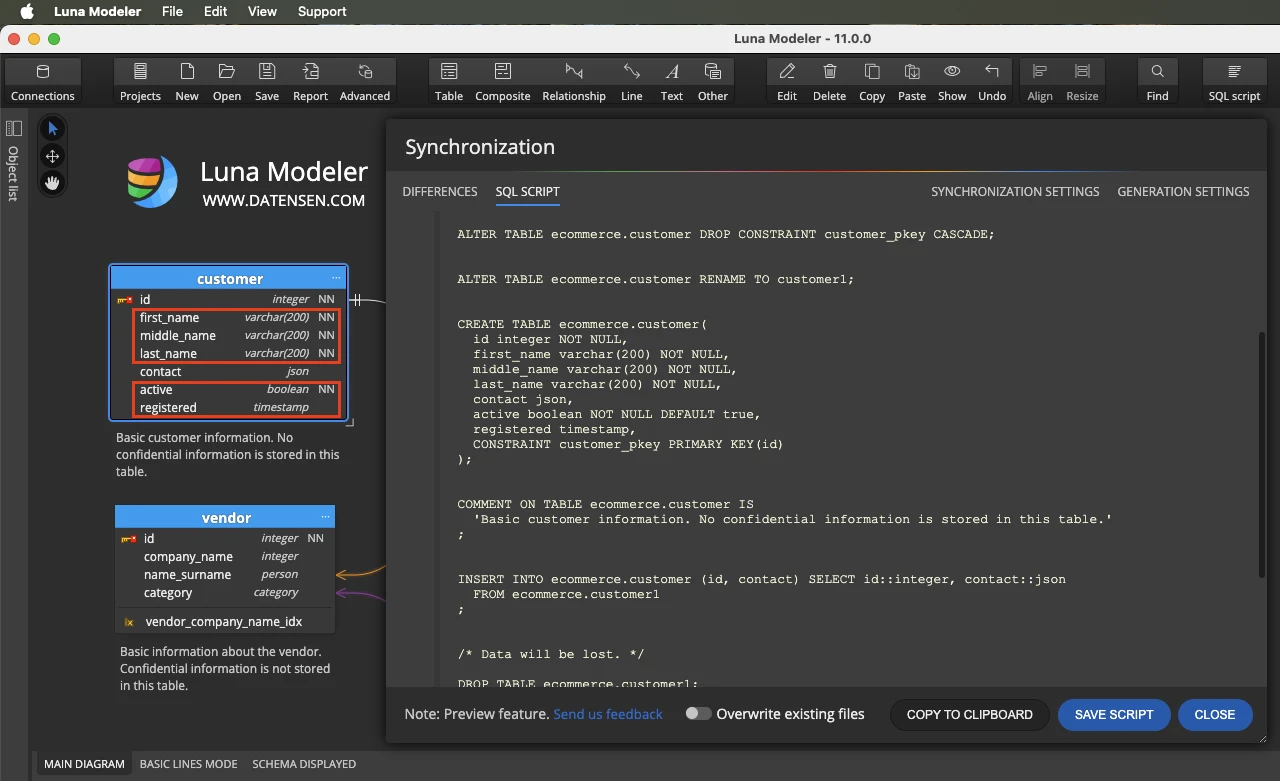
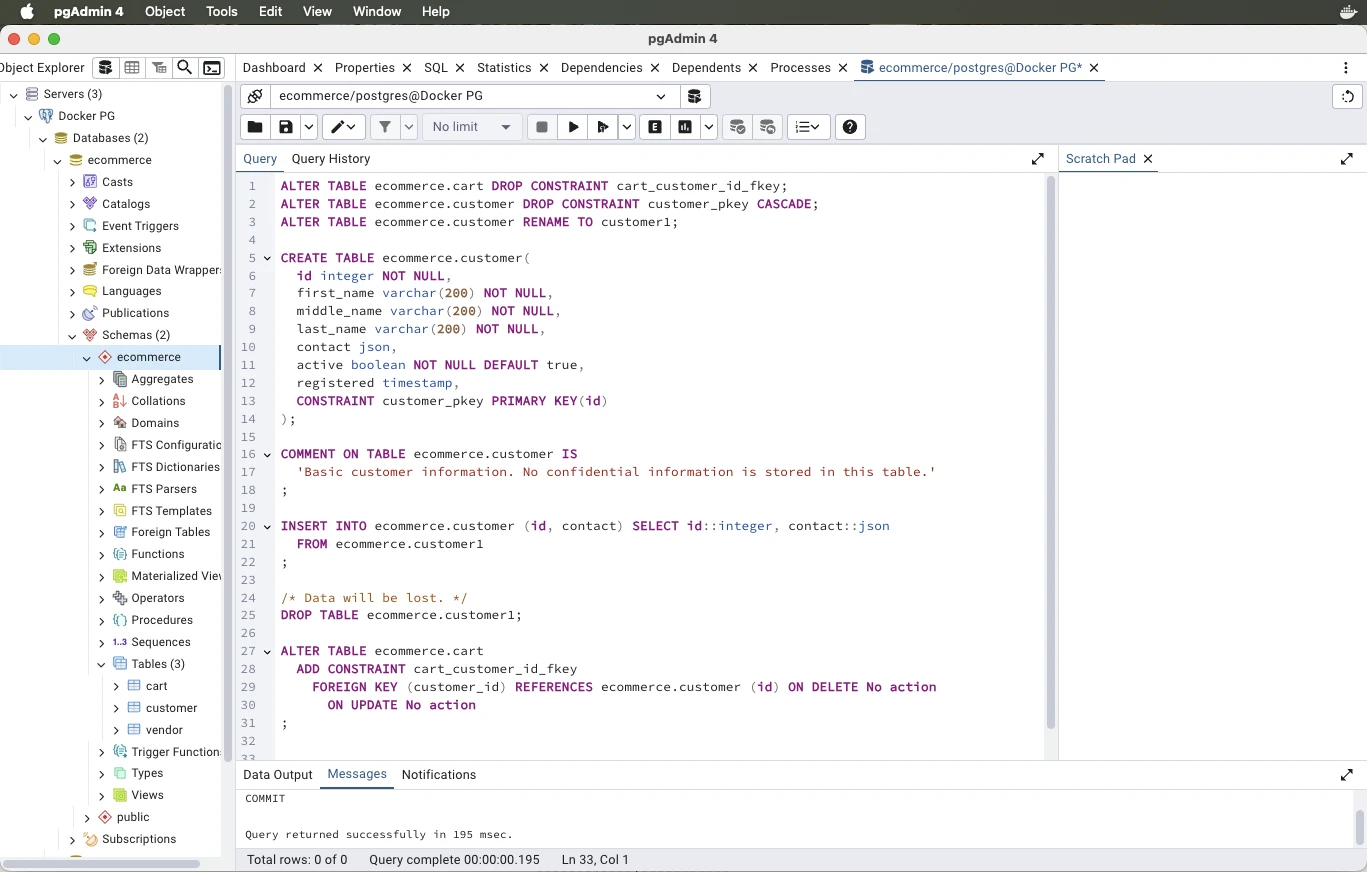
- Run Sync Script in pgAdmin
Start pgAdmin and open the Query Tool. Paste and execute the synchronization SQL script. Your live PostgreSQL database is now fully updated based on your visual data model.
Key Benefits of This Visual Workflow
- No command-line required – Everything runs through intuitive GUI apps
- Work offline on your model – Design first, deploy when ready
- Reliable and repeatable SQL generation – Generate and run SQL only when your model is complete
- Easy model-to-database synchronization – Quickly update your live database with visual changes
Get Started – Try Luna Modeler
#