In this article, we explain what a database entity is and describe other database elements.
Database entities
A database entity can be anything that exists in the real world such as a person, a book, a product, a company, an event, etc.

Attributes
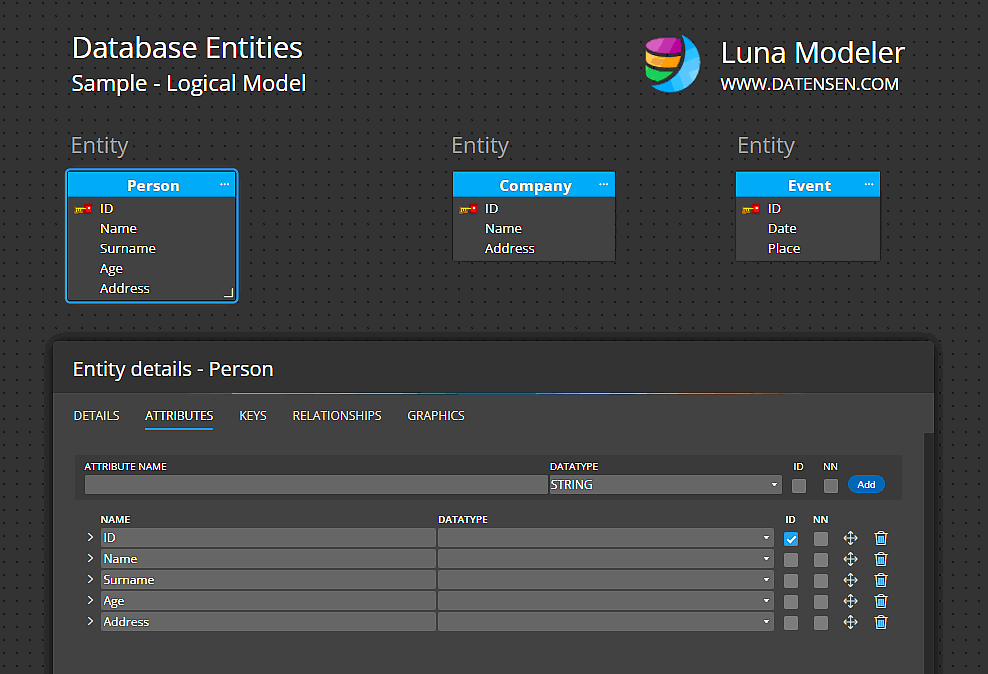
In the real world, almost everything has certain characteristics. In databases, the characteristics are represented by attributes. For example, a person entity may have attributes such as name, surname, age, contact information, address and others.
Relationships
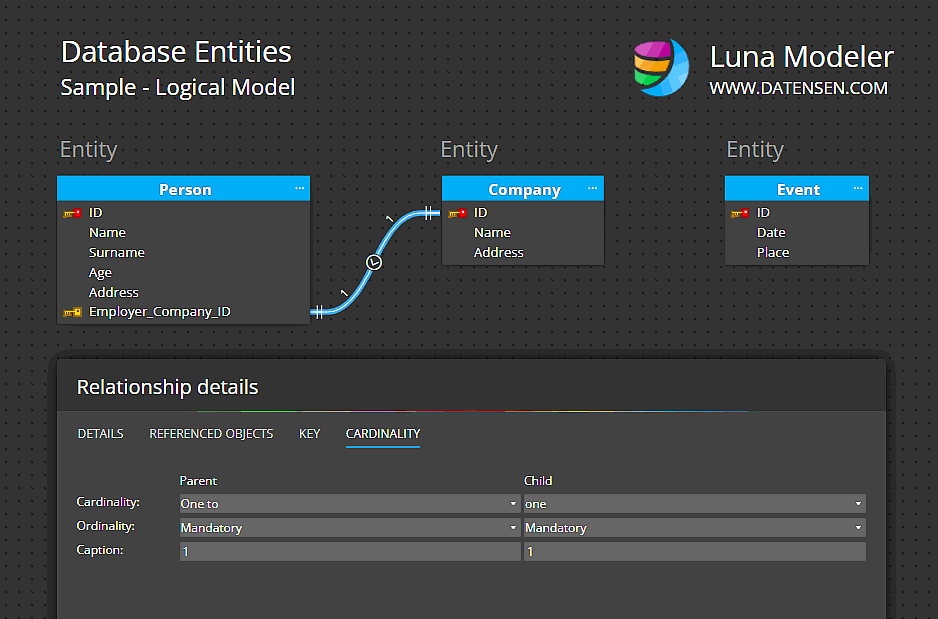
A database entity can also have relationships with other entities. A relationship is a connection between two or more entities. For example, a person entity may have a relationship with a company entity, indicating that the person works for the company.
How to design a database entity
To design a database entity, we need to identify the following elements:
- The name of the entity, which should be clear and descriptive.
- The attributes of the entity, which should capture the essential characteristics of the entity. Each attribute should have a name and a data type, such as string, integer, date, etc.
- The primary key of the entity, which should uniquely identify each instance of the entity. The primary key can be a single attribute or a combination of attributes.
- The relationships of the entity with other entities. Each relationship should have a name and a cardinality, such as one-to-one, one-to-many, many-to-many, etc.
Using data modeling tools
You can use data modeling tools such as Luna Modeler to conveniently design your database. The tool supports the creation of a logical model in which you can easily and comfortably visualize entities, attributes, relationships, and other information.
Conclusion
A database entity is a fundamental concept in database design and development. By following the steps of identifying, defining and designing database entities, we can create efficient and effective databases that meet our specifications.